P. Malag`o, L. Giovannini, R. Zivieri, P. Gruszecki and M. Krawczyk
Phys. Rev. B 92, 064416 (2015)
In this paper, we theoretically study the influence of a nonmagnetic spacer between ferromagnetic dots and a ferromagnetic matrix on the frequency dispersion of the spin-wave excitations in two-dimensional bicomponent magnonic crystals. By means of the dynamical matrix method we investigate structures that are inhomogeneous across the thickness represented by square arrays of cobalt or permalloy dots in a permalloy matrix. We show that the introduction of a nonmagnetic spacer significantly modifies the total internal magnetic field, especially at the edges of the grooves and dots. This permits the manipulation of the magnonic band structure of spin waves localized either at the edges of the dots or in matrix material at the edges of the grooves. According to the micromagnetic simulations two types of end modes were found. The corresponding frequencies are significantly influenced by the end modes’ localization region. We also show that, with the use of a single ferromagnetic material, it is possible to design a magnonic crystal preserving the properties of bicomponent magnonic crystals and magnonic antidot lattices. Finally, the influence of the nonmagnetic spacers on the technologically relevant parameters such as group velocity and magnonic bandwidth are discussed.
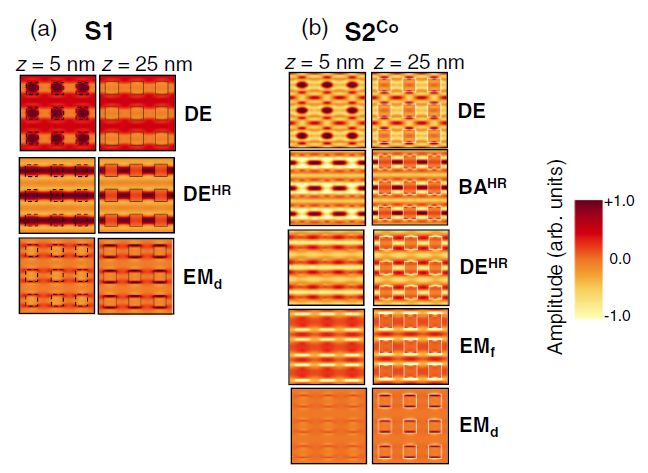
Fig.1. Spatial profiles (real part of the out-ofplane component of the dynamic magnetization vector) for spin waves with large differential scattering cross section in the center of the Brillouin zone. The spatial profiles of spin wave modes from the bottom part of the Py film (in the plane z = 5 nm in left column) and in the plane crossing dots (for z = 25 nm in right column) are shown in 3 × 3 primitive cells.